0 概述
Spring Cloud经验汇总
1 Spring Cloud Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway是微服务的网关,官网在这里,它的意义在于:
- 聚合多个微服务,提供单一的接入点,简化API的访问
- 接入处实现微服务的服务发现和路由,负载均衡,熔断降级
- 部署时的灰度发布,红绿部署
- 微服务的统一认证(常用),甚至授权(少用,授权更多使用单独的OAuth2来实现)
- 更适合动态刷新配置
Spring Cloud Gateway相对于nginx,更适合做业务层的分发操作。它一般放在nginx的后面。
Spring Cloud Gateway为了提高性能,采用了Reactive模式的Spring实现,代码看起来更加复杂,返回值是Mono<T>类型,而不是普通的Response类型。这点是与普通SpringBoot在编写业务规则中的最大不同点。
1.1 入门-Java配置路由
代码在这里
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>spring_test</groupId>
<artifactId>gatewayBasic</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>gatewayBasic</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.8</spring-cloud.version>
<start-class>spring_test.App</start-class>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.14</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-circuitbreaker-reactor-resilience4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>pom.xml的依赖配置,可以看到Spring Cloud是在Spring Boot的基础上加入更多的starter,并且在dependencyManagement中指定Spring Cloud的版本号。
/**
* Created by fish on 2021/3/15.
*/
server.port = 8111application.properties中只有端口配置
package spring_test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.MethodValidationPostProcessor;
/**
* Hello world!
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}入口也很简单
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator myRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
//curl http://localhost:8111/get,正常的拉取数据的方式
//curl --dump-header - --header 'Host: www.circuitbreaker.com' http://localhost:8111/delay/3, 模拟断线的方式
return builder.routes()
.route(p -> p
.path("/get")
.filters(f -> f.addRequestHeader("Hello", "World"))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.route(p -> p
.host("*.circuitbreaker.com")
.filters(f -> f.circuitBreaker(config -> config.setName("mycmd").setFallbackUri("forward:/fallback")))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.build();
}
}定义路由的网关,每一个route就是定义一条路由分发的规则。circuitBreaker就是熔断器了,可以在后端崩溃的时候,快速向前端返回错误,还可以指定熔断出现的时候对应的fallbackUri.
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@RestController
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping("/fallback")
public Mono<String> fallback() {
return Mono.just("fallback");
}
}定义fallback情况下的规则。
1.2 入门-yml配置路由
代码在这里
# curl http://localhost:8111/get,正常的拉取数据的方式
# curl --dump-header - --header 'Host: www.circuitbreaker.com' http://localhost:8111/delay/3, 模拟断线的方式
server:
port: 8111
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: addRequestHeader
uri: http://httpbin.org:80
predicates:
- Path=/get
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=Hello,World
- id: breakerCheck
uri: http://httpbin.org:80
predicates:
- Host=*.circuitbreaker.com
filters:
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: mycmd
fallbackUri: foward:/fallback我们使用yml来配置相同的效果,可以看到yml配置更加直观。predicates表达该路由的匹配规则。filter表达该路由匹配以后,需要执行的每个步骤。uri,是该路由的最开始的默认目的地,在filter里面可以修改这个目的地。
其他的地方和Java配置相似,只是没有了MainConfig文件而已。
1.3 限流
为了保护后端的微服务,我们需要对各个业务进行限流操作,以保护业务不会因为其中某些用户的访问过于频繁而拖垮。Spring Cloud Gateway自带了令牌桶算法来解决这个问题。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>加入redis的依赖项
# curl http://localhost:8111/get,正常的拉取数据的方式
# curl --dump-header - --header 'Host: www.circuitbreaker.com' http://localhost:8111/delay/3, 模拟断线的方式
server:
port: 8111
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
timeout: PT10S
password:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: rateLimit
uri: http://localhost:9199/
predicates:
- Path=/get
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20
redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1
key-resolver: "#{@defaultResolver}"注意,令牌桶算法中,replenishRate是令牌的补充速率,每秒往里面填充10个令牌。而burstCapacity是令牌桶的容量,令牌桶里面最多可以放置20个令牌。requestedTokens,是每个请求消耗多少个令牌,这些都是比较好理解。可以看这里
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ratelimit.KeyResolver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
public KeyResolver defaultResolver(){
return exchange -> {
return Mono.just(1+"");
};
}
@Bean
public KeyResolver randomResolver(){
return exchange -> {
return Mono.just(Math.ceil(Math.random()*100)+"");
};
}
//空字符串也会加入到RateLimiter测试里面
@Bean
public KeyResolver emptyResolver(){
return exchange -> {
return Mono.just("");
};
}
@Bean
public KeyResolver userParameterResolver(){
return exchange -> {
return Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("user"));
};
}
}预定义了多个KeyResolver,默认的KeyResolver是通过获取SecurityContext的Principle。
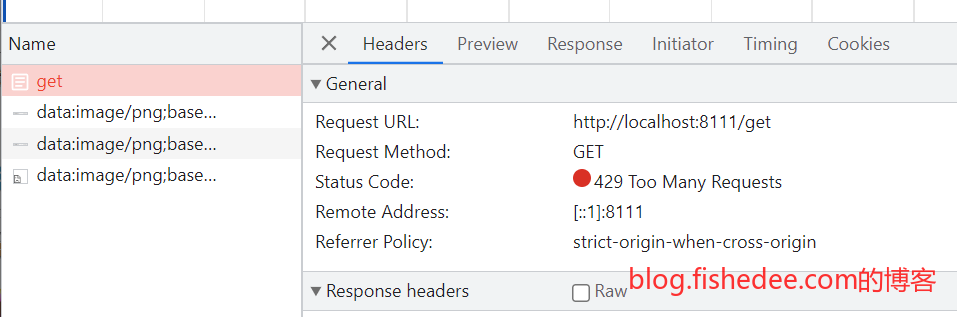
当请求量较频繁的时候,就会返回429的错误
1.4 自定义Predicates与Filter
1.4.1 工作流程
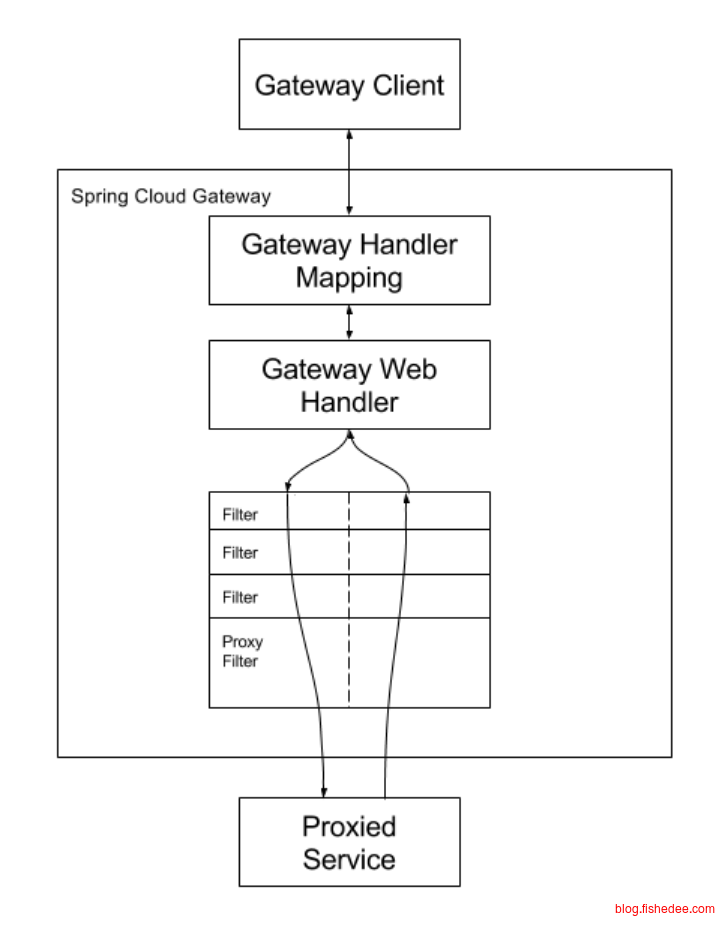
Spring Cloud Gateway的工作流程比较简单
- 一个Gateway有多个route
- 每个route,都有多个predicate,只有当多个preidcate都匹配的时候,才会选择执行这个route
- 选中执行这个route以后,就去执行这个route里面的多个filter
额外扩张概念,filter分为global filter与normal filter.
- global filter是所有route默认都需要执行的filter,有order选项,可以设置自己在执行链的序号,序号越小越靠前。ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter , RouteToRequestUrlFilter , NettyRoutingFilter,ForwardRoutingFilter , 都是以global filter的形式来实现的。
- normal filter是只有predicate匹配以后才会执行的filter,注意,没有order选项,看这里。RequestRateLimiter,CircuitBreaker, RewritePath, PrefixPath,等这些都是以normal filter的形式来实现的。
常见的global filter介绍
- RouteToRequestUrlFilter,从GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR中取出路由配置的uri字段,然后写入到目的地GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR中。它的order值为10000
- NettyRoutingFilter,从GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR中取出目的地,然后使用netty来发送到后端的服务器。它的order值为2147483647
其他的特性有:
总体而言,这种设计允许灵活多样的业务需要的,但是缺点是:
- 匹配route的时候,采用顺序匹配route的方式来实现,当route数量很多的时候,严重影响效率,现在主流的Gateway都采用基数树的方式来实现了。
- Spring Cloud Gateway采用WebFlux实现,这个实现并不是太成熟,依然有较多奇怪的问题,看这里
1.4.2 自定义global filter
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.net.URI;
import static org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CustomGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return chain.filter(exchange).doFinally(signalType -> {
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
HttpStatus statusCode = exchange.getResponse().getStatusCode();
URI url = exchange.getRequest().getURI();
log.info("Uri: {} | TargetUri:{} | HTTP Status: {} | Execution Time: {} ms ",
url,
exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR) ,
statusCode,
executionTime);
// Note: It's not possible to log response body without caching it first or reading it twice,
// which can impact performance. Be sure to consider these trade-offs before deciding to log response bodies.
});
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
}实现GlobalFilter接口就可以了,比较简单。这个global filter可以打印执行时间和结果。
package spring_test;
import org.reactivestreams.Publisher;
import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBuffer;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBufferUtils;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponseDecorator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CustomGlobalFilter2 implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
return chain.filter(exchange.mutate().response(decorateResponse(exchange.getResponse())).build());
}
private ServerHttpResponseDecorator decorateResponse(ServerHttpResponse response) {
return new ServerHttpResponseDecorator(response) {
@Override
public Mono<Void> writeWith(Publisher<? extends DataBuffer> body) {
if (body instanceof Flux) {
Flux<? extends DataBuffer> fluxBody = (Flux<? extends DataBuffer>) body;
return super.writeWith(fluxBody.map(dataBuffer -> {
byte[] content = new byte[dataBuffer.readableByteCount()];
dataBuffer.read(content);
DataBufferUtils.release(dataBuffer);
String responseBody = new String(content, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
// Here you can log the response body
log.info("Response body: {}" , responseBody);
return getDelegate().bufferFactory().wrap(content);
}));
}
return super.writeWith(body);
}
};
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
// It's important to return a lower value (higher priority) than NettyWriteResponseFilter (which has order -1),
// to ensure that our filter is executed before the response is written
return -2;
}
}如果要在Global filter中,由于WebFlux的设计问题,获取body内容的方式并不简单,需要重写writeWith方法。
1.4.3 自定义predicate
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.AbstractRoutePredicateFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
@Component
public class CheckTenantRoutePredicateFactory extends AbstractRoutePredicateFactory<CheckTenantRoutePredicateFactory.Config> {
public CheckTenantRoutePredicateFactory() {
super(Config.class);
}
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() {
return Collections.singletonList("tenantId");
}
//检查是否匹配路由
@Override
public Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(Config config) {
return exchange -> {
String queryValue = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("tenantId");
return config.getTenantId().equals(queryValue);
};
}
public static class Config {
private String tenantId;
public String getTenantId() {
return tenantId;
}
public void setTenantId(String tenantId) {
this.tenantId = tenantId;
}
}
}自定义一个Predicate,当query参数的tenantId的值与指定值匹配的时候,才进行路由。
shortcutFieldOrder 是 AbstractRoutePredicateFactory 类中的一个方法,用于定义你的配置类中的字段顺序。它在Spring Cloud Gateway中用于支持断言和过滤器的简写形式。
在一个路由配置中,断言和过滤器通常以键-值对的形式出现,如下面的例子所示:
yaml
Copy code
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: sample_route
uri: http://localhost:8080
predicates:
- Path=path:/sample/**, method:GET
在这个例子中,Path 断言有两个参数,一个是路径模式,另一个是请求方法。这种形式是完整形式,有时候会显得过于冗长。
为了让配置更简洁,Spring Cloud Gateway提供了一种简写形式。这就需要使用到 shortcutFieldOrder 方法。它返回一个字段名的列表,定义了这些字段在简写形式中的顺序。
例如,如果 shortcutFieldOrder 返回 ["pattern", "method"],那么我们就可以将上面的配置简写为:
yaml
Copy code
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: sample_route
uri: http://localhost:8080
predicates:
- Path=/sample/**, GET注意,shortcutFieldOrder的意思。
server:
port: 8111
spring:
cloud:
routes:
- id: customPredicate
uri: http://localhost:9199/
predicates:
- CheckTenant=fish
filters:
- RewritePath=/.*, /get2有了自定义Predicate以后,我们就能在yml里面进行使用了。注意,CheckTenant的名称来自于CheckTenantRoutePredicateFactory的类定义,后缀必须为RoutePredicateFactory。
1.4.4 自定义normal filter
package spring_test;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilter;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory.AbstractGatewayFilterFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBuffer;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
//全局Filter是不能设置Order的,看这里,https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-gateway/issues/1122
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DynamicServiceGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<DynamicServiceGatewayFilterFactory.Config>{
public DynamicServiceGatewayFilterFactory() {
super(DynamicServiceGatewayFilterFactory.Config.class);
}
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() {
return Arrays.asList("routes");
}
private Optional<String> findPath(ServerHttpRequest request,Config config){
String tenantId = request.getQueryParams().getFirst("tenantId");
List<TenantAndPathRoute> targetRoute = config.getRoutes().stream().filter(single->{
return single.getTenantId().equals(tenantId);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
if( targetRoute.size() == 0 ){
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.of(targetRoute.get(0).path);
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config){
return (exchange,chain)->{
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
Optional<String> path = this.findPath(request,config);
if( path.isPresent() == false ){
byte[] data = "{\"error\":\"无法找到路由\"}".getBytes();
DataBuffer buffer = response.bufferFactory().wrap(data);
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
response.getHeaders().add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(buffer));
}
try{
URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String newUriStr = originalUri.getScheme() + "://" +config.getHost() + path.get();
URI newUri = new URI(newUriStr);
log.info("newUri {} {}",newUri,originalUri);
ServerHttpRequest newRequest = request.mutate()
.uri(newUri)
.path(path.get())
.build();
ServerWebExchange newExchange = exchange.mutate()
.request(newRequest).build();
//写入旧目的地和新目的地
newExchange.getAttributes().put(CustomUriFilter.URI_KEY,newUri);
return chain.filter(newExchange);
}catch(URISyntaxException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
};
}
@Data
public static class TenantAndPathRoute{
private String tenantId;
private String path;
}
@Data
public static class Config {
// 控制是否开启认证
private List<TenantAndPathRoute> routes = new ArrayList<>();
private String host;
}
}我们尝试实现一个,动态设置目的地IP和url的filter。由于normal filter是不能修改order的,所以normal filter总是在RouteToRequestUrlFilter之前执行。而RouteToRequestUrlFilter总是会将route配置的默认uri写入到路由目的地中。因此,我们需要一个稍微弯曲的方法来实现我们的功能。
- 在normal filter里面,将我们的动态目的地写入到自定义的URI_KEY中
- 在RouteToRequestUrlFilter实现中,自动将route配置的默认uri写入到路由目的地中
- 自定义实现一个CustomUriFilter,它的order比RouteToRequestUrlFilter要大,将URI_KEY的动态目的地,覆盖RouteToRequestUrlFilter的配置,写入到最终目的地中
package spring_test;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.net.URI;
import static org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.RouteToRequestUrlFilter.ROUTE_TO_URL_FILTER_ORDER;
import static org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR;
@Component
public class CustomUriFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered{
public static final String URI_KEY = "com.spring_test.myRequest";
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
URI defineRequest = (URI)exchange.getAttributes().get(URI_KEY);
if( defineRequest != null ){
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR,defineRequest);
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return ROUTE_TO_URL_FILTER_ORDER+1;
}
}实现CustomUriFilter
server:
port: 8111
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
timeout: PT10S
password:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: customFilter
uri: no://op
predicates:
- Query=dynamic
filters:
- name: DynamicService
order: 10000
args:
host: localhost:9199
routes:
- tenantId: dog
path: /get3
- tenantId: cat
path: /get4我们最终实现了我们想要的效果,根据用户传入的参数,动态设置路由的目的地
1.5 配置优化
在这里中,我们知道,需要配置:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
httpclient:
connect-timeout: 200
response-timeout: PT10S
pool:
max-idle-time: PT10S
eviction-interval: PT30S不设置的话会导致空闲连接没有及时回收的问题
1.6 性能
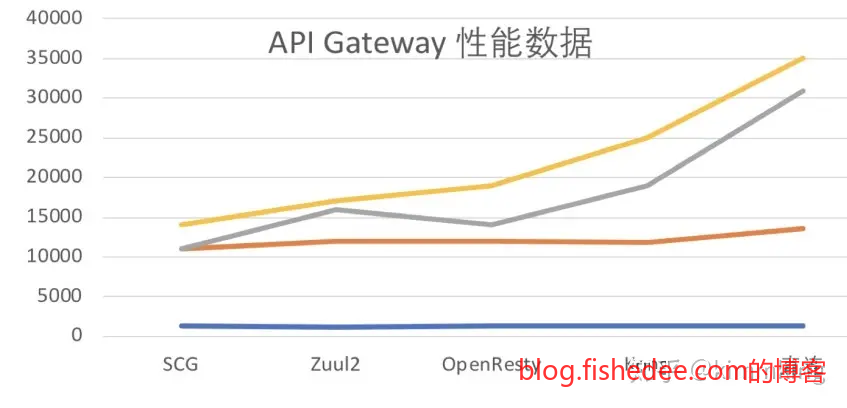
- 实测情况是性能 SCG~Zuul2 << OpenResty ~< Kong << Direct(直连);
- Spring Cloud Gateway(SCG)、Zuul2 的性能差不多,大概是直连的40%;但是Zuul2的周边生态较差,并发量大的时候报错很多。
- OpenResty、Kong 差不多,大概是直连的 60-70%;
看这里
1.7 小结
参考资料:
- 本文作者: fishedee
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 CN 许可协议,转载必须注明出处!