0 概述
dart语言,一个类似于TypeScript的语言,上手很快,有自己独特的特性
- 可靠的Null Safe系统
- 强大的模式匹配
- 很多的OOP支持
- 并发里面的isolate
官网在这里
1 快速上手
1.1 安装
安装flutter全家桶以后,就会自动安装dart语言
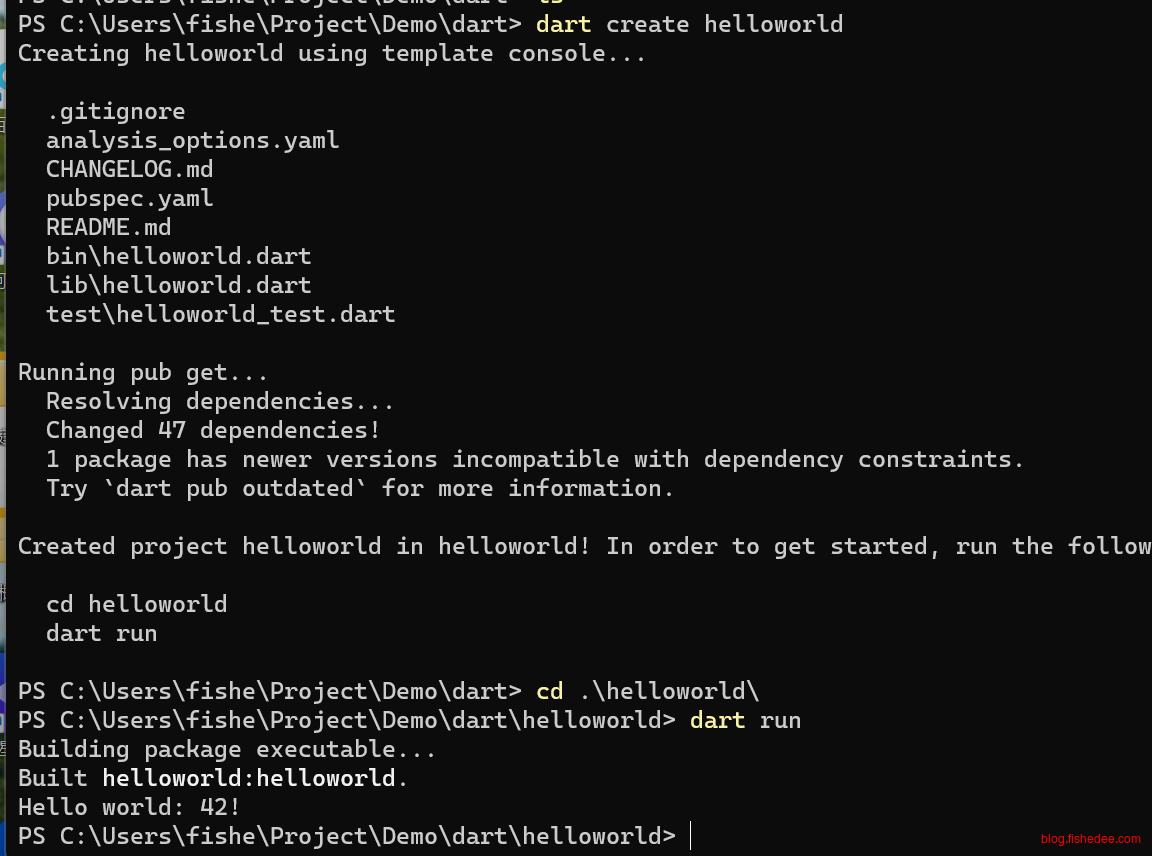
1.2 创建项目
dart create helloworld
cd helloworld
dart run比较简单,可以直接运行dart
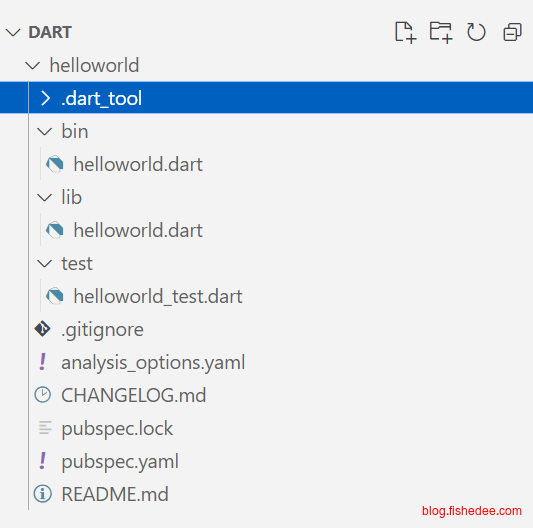
1.3 目录结构
生成的项目目录结构
name: helloworld
description: A sample command-line application.
version: 1.0.0
# repository: https://github.com/my_org/my_repo
environment:
sdk: ^3.2.4
# Add regular dependencies here.
dependencies:
# path: ^1.8.0
dev_dependencies:
lints: ^2.1.0
test: ^1.24.0pubspec.yaml,项目的配置文件,修改该配置文件,需要注意删掉.dart_tool,重新编译后才能生效。其中,name是项目名称,也是bin文件中的入口名称。
# This file configures the static analysis results for your project (errors,
# warnings, and lints).
#
# This enables the 'recommended' set of lints from `package:lints`.
# This set helps identify many issues that may lead to problems when running
# or consuming Dart code, and enforces writing Dart using a single, idiomatic
# style and format.
#
# If you want a smaller set of lints you can change this to specify
# 'package:lints/core.yaml'. These are just the most critical lints
# (the recommended set includes the core lints).
# The core lints are also what is used by pub.dev for scoring packages.
include: package:lints/recommended.yaml
# Uncomment the following section to specify additional rules.
# linter:
# rules:
# - camel_case_types
# analyzer:
# exclude:
# - path/to/excluded/files/**
# For more information about the core and recommended set of lints, see
# https://dart.dev/go/core-lints
# For additional information about configuring this file, see
# https://dart.dev/guides/language/analysis-optionsanalysis_options.yaml,静态分析的配置文件
import 'package:helloworld/helloworld.dart' as helloworld;
void main(List<String> arguments) {
print('Hello world: ${helloworld.calculate()}!');
}bin/helloworld.dart,入口文件
int calculate() {
return 6 * 7;
}lib/helloworld.dart,库文件夹
import 'package:helloworld/helloworld.dart';
import 'package:test/test.dart';
void main() {
test('calculate', () {
expect(calculate(), 42);
});
}test/helloworld.dart,单元测试文件夹
2 基础
代码在这里
2.1 类型
//只有int与double两种数值类型
//没有short,long,byte
//也没有float
testNumber(){
var a = 1; // 推导为int类型
var b = 2.2; // 推导为double类型
const c = 1; //常量声明
double d = 1; //显式类型声明
int e = 12;//显式类型声明
num f = 1e12;//声明num类型
a += 1;
b += 2;
e += 3;
print([a,b,c,d,e,f]);
}
testString() {
var a = 'aA'; // 推导为string类型
const b = 'b'; // 推导为string为b的类型
a += '1';
var c = 'Single quotes work well for string literals.';
var d = 'a:[$a]';//变量插入
var e = 'a:[${a.toUpperCase()}]';//调用变量的函数
var f = '''
You can create
multi-line strings like this one.
''';//多行文本
var g = r'In a raw string, not even \n gets special treatment.';//\n不转义,因为有r
print([a,b,c,d,e,f,g]);
}
testBoolean(){
var a = true;
var b = !false;
print([a,b]);
}
testDynamic(){
//dynamic编译时不检查,动态时检查,相当于typescript的any类型
dynamic c = 3;
//dynamic在编译时可以调用任意的方法,运行时进行匹配,下面代码运行时会报错
//c.toUppercase(2,3);
//这一句可以执行;
print('c is $c and isEven:${c.isEven}');
//dynamic 可以赋值为null类型
c = null;
print('c is $c when c is null');
}
testObject(){
//Object编译时检查,动态时不需检查,相当于typescript的unknown类型
Object d = 4;
//Object在编译时会进行检查,所有的类型都是Object类型,下面代码编译时会报错
//d.isEven
//有了is操作符判断以后就可以了
if( d is int){
print('d is $d and isEven:${d.isEven}');
}
//Object不能赋值为null类型,但Object?可以
//d = null;//报错
Object? d2 = 88;
d2 = null;
print('d2 is $d2 when d2 is null');
}
testTypeCheckAndConvert(){
Object a = 123;
//is和is!操作符
print('a is number = ${a is num}');
print('a is double = ${a is double}');
print('a is not string = ${a is! String}');
/* 以下代码报错,因为as类型转换失败
Unhandled exception:
type 'int' is not a subtype of type 'String' in type cast
*/
Object aStr = a as String;
print('a is str !');
}
testType(){
testNumber();
testString();
testBoolean();
testDynamic();
testObject();
testTypeCheckAndConvert();
}要点:
- 只有int与double两种数值类型,没有short,long,byte,char,也没有float
- 字符串支持插值,多行文本
- 有dynamic和Object两种类型
- 类型操作符有三个,as是强制类型转换,is和is!是类型判断
2.2 集合
testList(){
//推导为List<int>类型
var list = [1, 2, 3];
print(list);
//创建空数组
var list2 = List<int>.empty();
print(list2);
//增,删,改,查
list.add(4);
list.removeAt(0);
list[2] = 33;
print('list index 1 is ${list[1]}');
print('list length is ${list.length}');
//遍历
for( final item in list){
print('list item is :$item');
}
//list的控制流操作符
var mm = 44;
var list3 = [
...list,
for(var i = 0 ;i != 10;i++) i, //在集合加入for
if(mm<10) mm + 1, //在集合加入if
];
print('list3 $list3');
}
testSet(){
//推导为Set<string>类型
var set1 = {'a1', 'a2', 'a3'};
print(set1);
//创建空数组
var set2 = <int>{};
print(set2);
//增,删,改,查
set1.add('a4');
set1.remove('a2');
print('set has a1 is: ${set1.contains('a1')}');
print('set length is ${set1.length}');
//遍历
for( final item in set1){
print('set item is :$item');
}
//set的控制流操作符
var mm = 44;
var set3 = {
...set1,
for(var i = 0 ;i != 10;i++) 'a${i}', //在集合加入for
if(mm>10) '${mm + 1}', //在集合加入if
};
print('set3 $set3');
}
testMap(){
//推导为Set<string>类型
var map1 = {
'first1':'a1',
'first2':'a2',
'first3':'a3',
};
print(map1);
//创建空数组
var map2 = <int,String>{};
print(map2);
//增,删,改,查
map1['first4'] = 'a4';
map1.remove('first2');
map1['first1'] = 'a1111';
print('map has key first3 is: ${map1.containsKey('first3')}');
print('map length is ${map1.length}');
print('map value in key [first1] is ${map1['first1']}');
//遍历
for( final item in map1.entries){
print('map item is :${item.key} value:${item.value}');
}
//map的控制流操作符
var mm = 44;
var map3 = {
...map1,
for(var i = 0 ;i != 10;i++) 'first${i}':'b${i}', //在集合加入for
if(mm>10) 'mm':'${mm + 1}', //在集合加入if
};
print('map3 $map3');
}
testPositionRecord(){
print('-------- testPositionRecord ------');
//position record
var a = (1,'cc2');
(int,String) b;
b = a;
print([a,b,a==b]);
//record是immutable的,所有值不可修改
//a.$1 = 22
print('first is ${a.$1}, second is ${a.$2}');
}
testNameRecord(){
print('-------- testNameRecord ------');
//name record
var a = (age:11,name:'fish');
({int age,String name}) b;
b = a;
print([a,b,a==b]);
//name record比较的时候,名称也是一部分
var c = (age2:11,name:'fish');
print(a == c);
//record是immutable的,所有值不可修改
//a.$1 = 22
print('name is ${a.name}, age is ${a.age}');
}
testMixRecord(){
print('-------- testMixRecord ------');
var record = ('first', a: 2, b: true, 'last');
print('first : ${record.$1}, second : ${record.$2}');
print('a : ${record.a}, b : ${record.b}');
}
testCollection(){
testList();
testSet();
testMap();
testPositionRecord();
testNameRecord();
testMixRecord();
}要点如下:
- 四种集合类型,list, set , map和record。list用[],set和map用{},record用()
- 注意一下在list,set和map的初始化列表中,都支持spread operator,和嵌入if和for表达式
2.3 函数
//position 参数,[]是可选标记,里面可以填写默认值,对于nullable类型默认值就是null
int maxNumber(int a, int b,[bool? enableNegation,int defaultPlus=0]){
if(enableNegation != null && enableNegation ){
a = -a;
b = -b;
}
int result;
if( a> b){
result = a;
}else{
result = b;
}
return result + defaultPlus;
}
testPositionFunction(){
print('-------testPositionFunction---------');
print('${maxNumber(1,2)}');
print('${maxNumber(1,2,true)}');
print('${maxNumber(1,2,false,100)}');
}
//name参数,nullable参数可以不填写默认值,非nullable参数必须填写默认值。一种特殊情况是,非nullable参数不需填写默认值,但需要required标记。
int maxNumber2({required int left, required int right,bool? enableNegation,int defaultPlus=0}){
if(enableNegation != null && enableNegation ){
left = -left;
right = -right;
}
int result;
if( left> right){
result = left;
}else{
result = right;
}
return result + defaultPlus;
}
testNameFunction(){
print('-------testNameFunction---------');
print('${maxNumber2(left:1,right:2)}');
print('${maxNumber2(left:1,right:2,enableNegation:true)}');
print('${maxNumber2(left:1,right:2,enableNegation:false,defaultPlus:100)}');
}
//定义函数参数
int combineNumber(int left,int right,int Function(int left,int right) handler){
return handler(left,right);
}
//可以用typedef来定义函数参数类型
typedef HandlerType = int Function(int a, int b);
int combineNumber2(int left,int right,HandlerType handler){
return handler(left,right);
}
testLambada(){
print('-------testLambada---------');
//普通括号lambda是需要return
var c1 = combineNumber(1,2,(left,right){
return left+right;
});
//箭头lambda是立即value
var c2 = combineNumber(1,2,(left,right)=>left-right);
print('c1 = $c1,c2 = $c2');
}
testFunction(){
testPositionFunction();
testNameFunction();
testLambada();
}要点如下:
- position 参数,[]是可选标记,里面可以填写默认值,对于nullable类型默认值就是null
- name参数,nullable参数可以不填写默认值,非nullable参数必须填写默认值。一种特殊情况是,非nullable参数不需填写默认值,但需要required标记。
- 函数类型需要Function来标记,常用typedef来做类型别名。
- 创建lambda函数的时候,不需要=>符号,需要=>符号的话就是立即value的结构。
2.4 控制流
String testWhile(){
var out = "";
var a = 0;
while( a <= 10 ){
out = out + a.toString() +" ";
a++;
}
return out;
}
String testDoWhile(){
var out = "";
var a = 0;
do{
out = out + a.toString() +" ";
a++;
}while(a<=10);
return out;
}
String testFor(){
var out = "";
for( var a = 0 ;a<=10;a++){
out = out+a.toString() +" ";
}
return out;
}
String testForIn(){
var out = "";
for( var a in [1,2,3]){
out = out + a.toString() +" ";
}
return out;
}
testAlwaysCaptureVarInLoop(){
var callbacks = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
callbacks.add(() => print('call $i'));
}
for (final c in callbacks) {
c();
}
}
testLoop(){
print('testWhile: ${testWhile()}');
print('testDoWhile: ${testDoWhile()}');
print('testFor: ${testFor()}');
print('testForIn: ${testForIn()}');
print('testAlwaysCaptureVarInLoop: ${testAlwaysCaptureVarInLoop()}');
}
int testIf(int a,int b){
if( a > b ){
return a;
}else{
return b;
}
}
String testIfCase(Object input){
//if与模式匹配的组合,if case
if( input case (1,String _)){
return '(int 1 and String)';
}else if(input case(int _,String _)){
return '(int and String)';
}else{
return 'other';
}
}
testCondtion(){
print('testIf: ${testIf(33,44)}');
print('testIfCase (1,2): ${testIfCase((1,2))}');
print('testIfCase (\'cc\'): ${testIfCase('cc')}');
print('testIfCase (2,\'c2\'): ${testIfCase((2,'c2'))}');
print('testIfCase (1,\'c3\'): ${testIfCase((1,'c3'))}');
}
testSwitch(){
//switch表达式,可以获取值,而且自动进行Exhaustiveness checking
var a = 33;
var b = switch(a){
>10 => 'big',
==10 => 'middle',
<10 => 'little',
_ =>'unknown'
};
print('switch $a is $b');
//switch语句,可以带有独特的Guard clause,when语句,不匹配的话会fall through
var c = (111,33);
switch(c){
case (int a, int b) when a>b:
print('switch c is (a,b) and a > b');
case (int a,int b):
print('switch c is (a,b)');
}
}
testFlow(){
testLoop();
testCondtion();
testSwitch();
}要点:
- while/do while/for/ for in/if都是和js一样的做法。
- for的变量是always caputre的
- if case用来做模式匹配
- switch有两种用法,switch表达式,和switch语句,跟kotlin类似。这里的switch还带有独特的Guard clause语法。
2.5 异常
import 'dart:async';
testExceptionInner2(Function() handler){
try {
handler();
} on TimeoutException {
//只指定了捕捉的类型,不获取异常变量
print('timeout exception');
} on Exception catch (e) {
//既指定了捕捉的类型,也获取异常变量
//e 是Exception类型
print('Unknown exception: $e');
} catch (e,stack) {
//e 是Object类型,第二个参数固定为stack
print('Something really unknown: $e, stack: $stack');
//重新抛出异常
rethrow;
}finally{
print('finish');
}
}
testExceptionInner(){
print('-----------testExceptionInner-----------');
testExceptionInner2((){
throw new TimeoutException('cc');
});
testExceptionInner2(() {
throw new Exception('jj');
});
try{
testExceptionInner2((){
throw 'kk';
});
}catch(e){
}
}
testException(){
testExceptionInner();
}要点:
- 异常可以捕捉,或者取值两种操作,只是捕捉的话,用on就可以了。需要取值的话,还要加一个catch
- rethrow操作比较好,不影响原有的异常堆栈
- 任可以抛出任何类型的异常,但是建议只抛出Exception类型的异常。
2.6 模式匹配
testPatternUseCase(){
print('-----------testPatternUseCase-----------');
//变量声明
var (a1, [b1, c1]) = ('str', [1, 2]);
print('$a1 $b1 $c1');
//变量赋值
var (a2, b2) = ('left', 'right');
(b2, a2) = (a2, b2); // Swap.
print('$a2 $b2');
//switch表达式
dynamic obj = 1;
switch (obj) {
// Matches if 1 == obj.
case 1:
print('one');
// Matches if the value of obj is between the
// constant values of 'first' and 'last'.
case >= 10 && <= 20:
print('in range');
// Matches if obj is a record with two fields,
// then assigns the fields to 'a' and 'b'.
case (var a, var b):
print('a = $a, b = $b');
default:
}
//for表达式
Map<String, int> hist = {
'a': 23,
'b': 100,
};
for (var MapEntry(key: key, value: count) in hist.entries) {
print('$key occurred $count times');
}
//if case表达式
Object input = (1,'33');
if( input case (1,String _)){
print('(int 1 and String)');
}else if(input case(int _,String _)){
print('(int and String)');
}else{
print('other');
}
//也能用于json校验
Object json = {'user':['fish',123],'user2':['bb',456]};
if (json case {'user': [String name, int age]}) {
print('User $name is $age years old.');
}
}
testPatternMatchValue(){
print('-----------testPatternMatchValue-----------');
var handler1 = ((Object? a){
const jj = (1,'cc');
switch(a){
case 10:
print('10');
case 'cc':
print('cc');
case null:
print('null');
case jj:
print('match constant jj');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
handler1(10);
handler1('cc');
handler1(null);
handler1((1,'cc'));
handler1({'c'});
}
testPatternMatchCast(){
print('-----------testPatternMatchCast-----------');
var handler1 = ((dynamic a){
switch(a){
//只有非空时才匹配,空的时候不匹配,也不抛异常
case var a1?:
print('a1 is not null');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
handler1(10);
handler1(null);
var handler2 = ((dynamic a){
switch(a){
//非空与空时都匹配,空的时候会抛异常,相当于cast为非空类型。
case var a1!:
print('a1 must nullable');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
handler2(10);
//以下语句会抛出异常,因为a1!匹配遇到null,会抛出异常
//handler2(null);
var handler3 = ((dynamic a){
switch(a){
//非空与空时都匹配,空的时候不抛异常
case var a1:
print('a1 is null or not-null');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
handler3(10);
handler3(null);
var handler4 = ((dynamic a){
switch(a){
//非空时,匹配a1,且cast为String类型,如果cast失败,会抛出异常
case var a1 as String:
print('a1 must String');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
//以下语句会抛出异常,因为a1匹配遇到到非string,会抛出异常
//handler4(10);
handler4('bb');
}
class MyRect{
int x;
int y;
int width;
int height;
MyRect({required this.x,required this.y, required this.width, required this.height});
}
testPatternMatchType(){
print('-----------testPatternMatchType-----------');
var handler1 = ((Object object){
switch(object){
case int a:
print('int $a');
case [var a, var b]:
print('lsit: two [$a,$b]');
case [var a, ...var rest, var b]:
print('list: three or more, inner is $rest');
case {"name":String name}:
print('map: name with String value: $name');
case {"name":var name}:
print('map: name with any value: $name');
case (var first,var second):
print('record: position (first,second)');
case (name1:var name1,name2:var name2):
print('record: name($name1,$name2)');
case MyRect(width:var width,height: var height)://通过object的getter来抽取变量
print('myRect: width = $width,height = $height');
case _:
print('other');
}
});
handler1(123);
handler1([1,2]);
handler1([1,2,3,4,5,6,7]);
handler1({"name":"fish","age":123});
handler1({"name":520});
handler1(('fish',123));
handler1(('fish',123,true));//不能匹配(var first,var second)
handler1((name1:'jj',name2:'kk'));
handler1((name1:'jj',name2:'kk',name3:'uu'));//不能匹配(name1:var name1,name2:var name2)
handler1(MyRect(x:1,y:1,width:100,height:200));
}
testPatternMatchRelation(){
print('-----------testPatternMatchRelation-----------');
var handler1 = ((int char){
const space = 32;
const zero = 48;
const nine = 57;
const a = 97;
const A = 65;
switch (char) {
case < space:
print('control');
case == space:
print('space');
case > space && < zero:
print('punctuation');
case >= zero && <= nine:
print('digit');
case == a || == A:
print('alpha A/a');
default:
print('other');
};
});
handler1(' '.codeUnitAt(0));
handler1('\t'.codeUnitAt(0));
handler1('2'.codeUnitAt(0));
handler1('a'.codeUnitAt(0));
handler1('你'.codeUnitAt(0));
}
//pattern是类型与值的组合匹配工具,
//匹配以后还能进行cast操作,cast为非空类型,或者cast为指定类型,如果cast失败就会抛出异常
//匹配与cast以后还能解构取值
testPattern(){
testPatternUseCase();
testPatternMatchValue();
testPatternMatchType();
testPatternMatchCast();
testPatternMatchRelation();
}dart的模式匹配是看家本领,主要用于:
- 变量声明
- 变量赋值
- switch表达式
- for表示解构,严格来说这个也属于变量声明
- if case表达式,这个用来做输入数据校验,简直一流。NICE。
dart的模式匹配有如下几种目的:
- 匹配常量,只有常量才能匹配,任何const的值。
- 匹配类型,list,set,map,record的组合类型,相当强大方便。当然也包括空与非空的匹配,
- 组合匹配,包括,且,或,子匹配。
- 类型cast,匹配成功以后,可以进行类型cast。包括强行指定非空,强行转换到目标类型。
- 解构变量,匹配成功以后,可以解构取出一部分的value,以便进行下一步的操作。
3 类
代码在这里
3.1 基础
//默认是不可以被继承的
class Person {
//默认为public,自动有getter和setter
var name = "fish";
var age = 123;
//final变量,只能在赋值,或者构造函数赋值,一旦赋值以后就无法更改
final int height;
Person(this.height);
//下划线开头的是私有变量,没有getter,也没有setter
//自定义getter与setter
//getter与setter的名字不能与filed的名字一致
var _color = "red";
String get color{
print("color getter run");
return _color;
}
set color(String value) {
print("color setter run");
_color = value;
}
//late变量在运行时检查null方式
late int width;
//late + final,运行时检查null方式,运行时检查仅赋值一次
late final int kk;
eat(){
print("$name is eating. He is $age years old. height = $height, width = $width, color = $_color ");
}
}classBasicInner.dart文件。
import './classBasicInner.dart';
testClassBasic(){
var p = Person(33);
print('person: name = ${p.name} , age = ${p.age} ,height = ${p.height} color = ${p.color}');
p.age = 121;
p.name = "Fish";
//以下语句在编译时报错,因为_color是私有变量
//print('${p._color}');
//以下语句在编译时保存,因为height是final变量,不能修改
//p.height = 33;
//color是setter方法,不是真实的变量
p.color = 'green';
//以下语句在运行时报错,因为width是late变量,width还没初始化就执行getter
//print(p.width);
p.width = 100;
print('width = ${p.width}');
p.kk = 8;
//以下语句在运行时报错,因为kk是late + final变量,不能二次赋值
//p.kk = 9;
//调用方法
p.eat();
}要点如下:
- 默认的公共变量,自动生成getter与setter
- 私有变量,是约定以下划线开头的变量。只能在同一个文件访问,不能在外部访问。依然会生成getter与setter。
- const是编译时常量。
- final是运行时常量,一旦赋值就不能修改。
- 默认是编译是检查变量的null方式,变量只能在声明处,构造函数参数列表,初始化参数列表,这三个地方赋值。注意,不在构造函数的body进行赋值检查。
- late是运行时检查null的方式,和kotlin的类似。
- late + final,是运行时检查常量 + 运行时检查null。
3.2 构造函数
class Shape{
String _name;
Shape({String name = 'default'}):_name = name;
}
String prefixName(String name){
return "prefix_$name";
}
double addTen(double a){
return a+10;
}
//继承
class Point extends Shape {
double x = 0;
double y = 0;
//参数上直接用this来指定变量,无名称的是默认构造函数
//这里使用了position parameter
Point(this.x, this.y);
//默认构造函数只有一个,第二个构造函数,需要名字,例如这个origin名字
//这里使用了name parameter
Point.origin({required this.x, required this.y});
//使用初始化列表来初始化参数
Point.origin2({required double x1, required double y1})
: x = x1,
y = y1;
//调用同级的构造函数
Point.diag(double x): this(x,x);
//调用父级的构造函数
Point.withName(String name,this.x,this.y):super(name:name);
//调用父级的构造函数,初始化列表允许使用函数
Point.withName2(String name,this.x,this.y):super(name:prefixName(name));
//私有的构造函数,外部不能调用
Point._my(this.x,this.y):super(name:'_myPoint'){
print('_my constructor init');
}
//工厂构造函数,有完善的构造体,可以对参数进行任意转换,返回值必须是Point,不能为null
factory Point.shiftTen(double x,double y){
return Point._my(x+10,y+10);
}
//覆盖方法
@override
String toString() {
return 'Point(x:$x,y:$y,name:${super._name})';
}
}
//不可变的类型
class ImmutablePoint{
//不可变类型的变量都必须是final
final double x;
final double y;
const ImmutablePoint(this.x,this.y);
//不可变类型的初始化列表,不能使用函数,以下语句编译时报错
//const ImmutablePoint.gg(x2,y2):x = x2,y = addTen(y2);
}
testClassConstruct(){
//构造函数可以不需要new关键字
var a = new Point(10,10);
var b = new Point.origin(x: 20, y: 20);
var c = Point.origin2(x1: 30, y1: 30);
var d = Point.withName("g1", 40,50);
var e = Point.withName2("g2",60,70);
var f = Point.diag(80);
//工厂构造函数的调用,和普通构造函数是一样的
var g = Point.shiftTen(90, 90);
print('testClassConstruct a = $a, b = $b , c = $c, d = $d, e = $e , f = $f , g = $g');
}要点如下:
- 默认构造函数只有一个,其他构造函数都需要带有名字。
- 成员变量默认是编译时检查变量的null方式,变量只能在声明处,构造函数参数列表,初始化参数列表,这三个地方赋值。注意,不在构造函数的body进行赋值检查。
- 工厂构造函数,可以做更多复杂的构造方式。
- 常量的类,成员变量必须是final,并且初始化构造函数不能使用函数。
- 有很多多样的变量赋值方式,具体看Demo。
3.3 方法
import 'dart:math';
abstract interface class IMap{
dynamic operator[](String name);
void operator[]=(String name ,dynamic target);
}
class Point implements IMap{
double x;
double y;
static int _instanceCount = 0 ;
static incInstanceCount(){
_instanceCount++;
}
static getInstanceCount(){
return _instanceCount;
}
Point(this.x, this.y){
incInstanceCount();
}
double distanceTo(Point other) {
var dx = x - other.x;
var dy = y - other.y;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
//操作符重载
Point operator +(Point v) => Point(x + v.x, y + v.y);
Point operator -(Point v) => Point(x - v.x, y - v.y);
Map<String,dynamic> myMap = {};
@override
dynamic operator[](String name){
print('get operator $name');
return myMap[name];
}
@override
void operator[]=(String name ,dynamic target){
print('set operator [] $name = $target');
myMap[name] = target;
}
//override接口
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
other is Point && x == other.x && y == other.y;
//getter与setter
double get sum{
return x + y;
}
set sum(double value){
if( value != 0 ){
throw Exception('must be zero');
}
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
@override
int get hashCode => Object.hash(x, y);
@override
String toString(){
return 'Point(x=$x,y = $y)';
}
}
testClassMethodBasic(){
var point = Point(1,2);
point.sum = 0;
point.x = 10;
point.y = 20;
var point2 = point+point;
IMap map = point2;
map['name'] = 'fish';
print('map name is ${map['name']}');
print('point = $point, point2 = $point2, if point == point2 : ${point==point2}');
print('point to point2 distance = ${point.distanceTo(point2)}');
print('point instance count: ${Point.getInstanceCount()}');
}
extension isBlankString on String {
bool get isBlank => trim().isEmpty;
}
testClassMethodExtension(){
var mm = 'cc';
print('$mm is blank = ${mm.isBlank}');
}
class WannabeFunction {
//直接用call来创建对象即可
String call(String a, String b, String c) => '$a $b $c!';
}
testClassMethodCallable(){
var wf = WannabeFunction();
var out = wf('Hi', 'there,', 'gang');
print('WannabeFunction is $out');
}
testClassMethod(){
testClassMethodBasic();
testClassMethodExtension();
testClassMethodCallable();
}要点有:
- 有static的变量和方法,以及普通的成员方法
- 有getter/setter的方法
- 有操作符重载的方法,支持加减乘除,方括号索引和设置
- 覆盖父级方法的话,可以加入@override标记
其他特性:
3.4 接口
//定义抽象类
abstract class Square{
//定义抽象方法,无需abstract前缀
String getName();
}
//每个类,都是一个接口
//extends继承
class Circle extends Square{
//override 覆盖方法
@override
String getName(){
return 'circle';
}
double _radius;
Circle(this._radius);
double getRadius(){
return _radius;
}
}
//实现接口,用implements,建议不要使用class直接用interface,这样连私有变量的getter/setter都需要实现。
class MCricle extends Square implements Circle{
//私有变量_radius的getter/setter都需要实现。
@override
double get _radius{
return _radius2;
}
@override
set _radius(double value){
_radius2 = value;
}
double _radius2;
MCricle(this._radius2);
@override
double getRadius(){
return _radius2;
}
@override
String getName(){
return 'mcircle';
}
}
//需要用abstract interface,才能实现Kotlin中的interface中意义。
abstract interface class ShapeInterface{
double getRadius();
String getName();
}
class MCircle2 implements ShapeInterface{
double _radius2;
MCircle2(this._radius2);
@override
double getRadius(){
return _radius2;
}
@override
String getName(){
return 'mcircle2';
}
}
//定义一个mixin类,并且要求使用这个mixin的类都需要实现SquareInterface接口,on是可选操作
//相当于kotlin中的by,有自己的变量和方法
mixin ColorShape on ShapeInterface{
String color = "red";
debugInfo(){
print('Square name is ${getName()} , radius is ${getRadius()}, color is $color');
}
}
//实现shape接口,并且使用ColorShape的with
class ColorSquare extends ShapeInterface with ColorShape{
@override
double getRadius(){
return 50;
}
@override
String getName(){
return 'colorSquare';
}
}
testClassInterface(){
var circle = Circle(11);
print('circle radius is ${circle.getRadius()},name is ${circle.getName()}');
var circle2 = MCricle(12);
print('circle2 radius is ${circle2.getRadius()},name is ${circle2.getName()}');
ShapeInterface circle3 = MCircle2(10);
print('circle3 radius is ${circle3.getRadius()},name is ${circle3.getName()}');
var square = ColorSquare();
square.color = 'blue';
square.debugInfo();
}要点:
- 每个类,都是一个接口
- extends是继承,implements是实现接口。建议不要使用class直接用interface,这样连私有变量的getter/setter都需要实现。推荐使用abstract interface,才能实现Kotlin中的interface中意义。
- mixin是相当于Kotlin里面的by委托。mixin类有自己的成员变量和成员方法,而且可以指定使用者必须满足的类型要求,on约束。
3.5 类修饰符
//abstract, 抽象类,没啥好说的
abstract class Vehicle {
void moveForward(int meters);
}
//base, 只能继承,不能实现接口
base class Vehicle2 {
void moveForward(int meters) {
}
}
//interface,只能实现接口,不能继承
interface class Vehicle3 {
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}
//final,不能继承,也不能实现接口
final class Vehicle4 {
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}
//sealed类,和kotlin的一样
sealed class Vehicle5 {}
class Car extends Vehicle5 {}
class Truck implements Vehicle5 {}
class Bicycle extends Vehicle5 {}
testClassSealed(){
// ERROR: Cannot be instantiated
//Vehicle myVehicle = Vehicle5();
// Subclasses can be instantiated
Vehicle5 myCar = Car();
//sealed类的好处是,switch的时候,可以进行exhaustively matched检查
/*
String getVehicleSound(Vehicle vehicle) {
// ERROR: The switch is missing the Bicycle subtype or a default case.
return switch (vehicle) {
Car() => 'vroom',
Truck() => 'VROOOOMM',
};
}
*/
}
testClassModifier(){
testClassSealed();
}要点如下:
- abstract, 抽象类,没啥好说的
- base, 只能继承,不能实现接口
- interface,只能实现接口,不能继承
- final,不能继承,也不能实现接口
- sealed类,和kotlin的sealed是一样
3.6 枚举
enum Color {
red('红色'),
green('绿色'),
blue('蓝色');
//构造函数必须是const的,因此成员变量也必须是final的
final String label;
const Color(this.label);
@override
String toString(){
//每个枚举都有一个index
return 'color:$label, index $index';
}
}
testClassEnum(){
var color1 = Color.red;
print('color1 = $color1');
//默认有values,可以获取所有枚举值
var allColors = Color.values;
print('allColors = $allColors');
}要点如下:
- 枚举必须是const 构造函数的。
- FIXME,枚举作为输入变量,反序列化不存在的时候怎么办,会报错吗?
4 泛型
//泛型函数
T printTemp<T>(T a){
print('${a}_temp');
return a;
}
//extends指定了泛型的上界
T printTemp2<T extends num>(T a){
print('${a}_temp2');
var c = a+1;
//dart的泛型是运行时泛型,所以可以用is T的操作
if( c is T){
return c;
}
throw Exception('invalid $c');
}
//默认泛型参数为T的时候,允许传入nullable类型
//使用T extends Object的时候,不允许传入nullable类型
class SimpleData<T extends Object>{
T? _data;
set(T t){
_data = t;
}
T? get(){
return _data;
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
Person(this.name,this.age);
}
class Man extends Person{
Man(super.name,super.age);
}
testGeneric(){
printTemp(null);
printTemp(1);
printTemp('abc');
printTemp2(12);
printTemp2(12.3);
var data1 = SimpleData<int>();
data1.set(123);
print("data1 ${data1.get()}");
var data2 = SimpleData<Person>();
data2.set(Person("cat",879));
print("data2 ${data2.get()}");
//这里会报错,因为类型不匹配
//data2.set(123)
//这里会报错,因为不能使用nullable类型
//var data3 = SimpleData<Person?>();
//dart中没有协变,和逆变的说法,所以以下代码
//编译时没有问题,但是运行时报错
//在Kotlin中,不可变数组才是协变,才能允许将List<Man>赋值到List<Person>的。可变数组不是协变,不允许这样赋值的,在编译时确定错误
List<Man> list = List.empty();
List<Person> list2 = list;
list2.add(Person('cc',33));
}要点:
- 支持泛型方法和泛型类
- 使用extends关键字来做泛型约束,这点和TypeScript是一样的。
- 运行时泛型实现,不是Java的编译时实现(运行时擦除泛型)
- 没有协变和逆变系统,这点略有缺失,运行时可能会产生错误。Kotlin中有协变和逆变系统
5 异步
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:isolate';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
//async和await执行,相当简单
testHttpRequest() async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('http://www.baidu.com/'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
// 请求成功,你可以处理响应的数据
print('Response data: ${response.body}');
} else {
// 请求失败,处理错误信息
print('Failed to load data. Status code: ${response.statusCode}');
}
}
//在async中切换到其他线程执行,将结果发射回来
int slowFib(int n) => n <= 1 ? 1 : slowFib(n - 1) + slowFib(n - 2);
void testIsolateRun() async {
var result = await Isolate.run(() => slowFib(10));
print('Fib(10) = $result');
}
//参考这里的范例,https://dart.dev/language/isolates
void testCompleter() async {
//completer,需要在同一个isolate中使用,不能在不同isolate之间传递
final completer = Completer<int>();
//不同isolate之间只能使用SendPort和ReceivePort来传递信息
final receivePort = ReceivePort();
//启动Isolate,不同Isolate之间内存也是不共享的
await Isolate.spawn(_isolatedFunction, receivePort.sendPort);
//侦听结果信息
receivePort.listen((data) {
if (data is int) {
completer.complete(data);
} else if (data is String) {
completer.completeError(data);
}
});
//等待completer的结果
var result = await completer.future;
print('Fib2(20) = $result');
//关闭receivePort,从而让listen关闭。并且isolate停止,才能让程序退出
receivePort.close();
}
void _isolatedFunction(SendPort sendPort) {
// This is executed in the spawned isolate
try {
var result = slowFib(20);
sendPort.send(result); // Sending the result back to the main isolate
} catch (e) {
sendPort.send('Error: $e'); // Sending an error message back to the main isolate
}
}
testAsyncBasic(){
//testHttpRequest();
testIsolateRun();
testCompleter();
}要点如下:
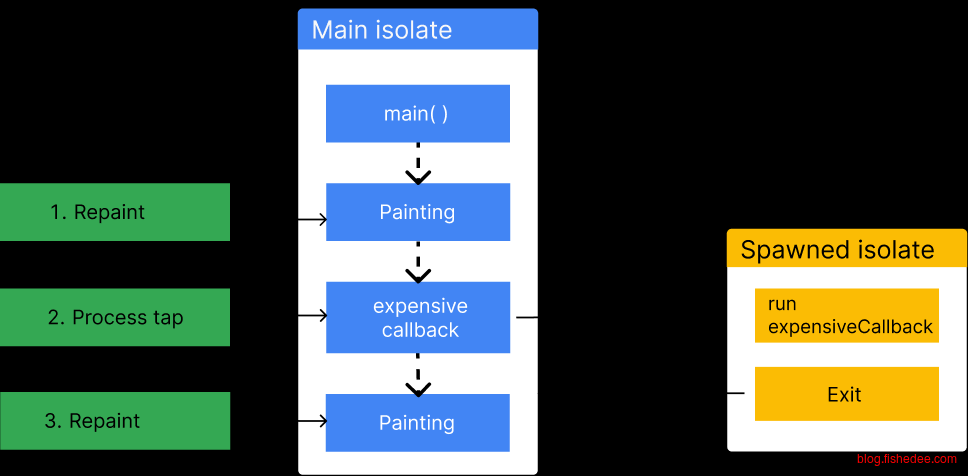
- isolate是独特的异步系统,每个isolate的内存是隔绝的。使用ReceivePort和SendPort来传递。各自的isoltate之间有事件循环。
- 异步方法使用async/await来标记就可以了,这点和js是一样的。
- 自定义异步方法的话,可以用Completer来实现。
- 使用Isolate.run来切换到后台线程来执行代码。
6 非空安全性
import 'dart:math';
bool random(){
double randomDouble = Random().nextDouble();
return randomDouble<0.5;
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
Person(this.name,this.age);
}
testNullBasic(){
List<int>? a;
if( random()){
a = [1,2,3];
}
Person? b;
if( random()){
b = Person('fish',123);
}
print('a is $a and a[0] is ${a?[0]}');
print('b is $b and a.name is ${b?.name}');
//两个句号组成的,可以让返回值变为b本身,方便串联多个操作
b?..name = 'cat'
..age = 234;
print('after b is $b and a.name is ${b?.name}');
}Dart是sound null safety系统,为此,它作出了很多努力,可以看这里
7 工具
dart pub add xxx添加依赖
dart pub remove xxx删除依赖
dart run启动
具体可以看这里
10 总结
dart语言中优秀的地方:
- 优秀的sound null safety类型系统
- 优秀的模式匹配工具,可以简洁精确地表达类型
- 严谨的final和const的区分,final是运行时不可变,const是编译时不变。只有const变量才能放在switch表达式中进行匹配。(暂时没有在其他语言中看到对final和const区分如何严谨的特性)
- for和if放在集合表达式中,语法糖挺好
- isolate的设计很适合UI系统,而且不容易产生并发修改同一个变量的情况,UI系统用这个设计非常好。
- 编译时泛型系统
- 同时支持AOT和JIT
不太好的地方:
- 所有的类默认都是一个interface,真是糟糕透了。
- 所有成员变量,公开的都自动生成getter/setter方法,甚至无法屏蔽其中之一。这个设计最差,类最大优点就是封装性,默认生成setter毫无封装性可言。而且,私有变量,在外部文件无法访问它的getter/setter,我还得手写一次getter,也很麻烦。(为啥没有只生成getter,不生成setter的默认配置)
- 没有反射, toString, hashCode, json序列化都不好做。
- 没有TypeScript的类型运算和判断操作。
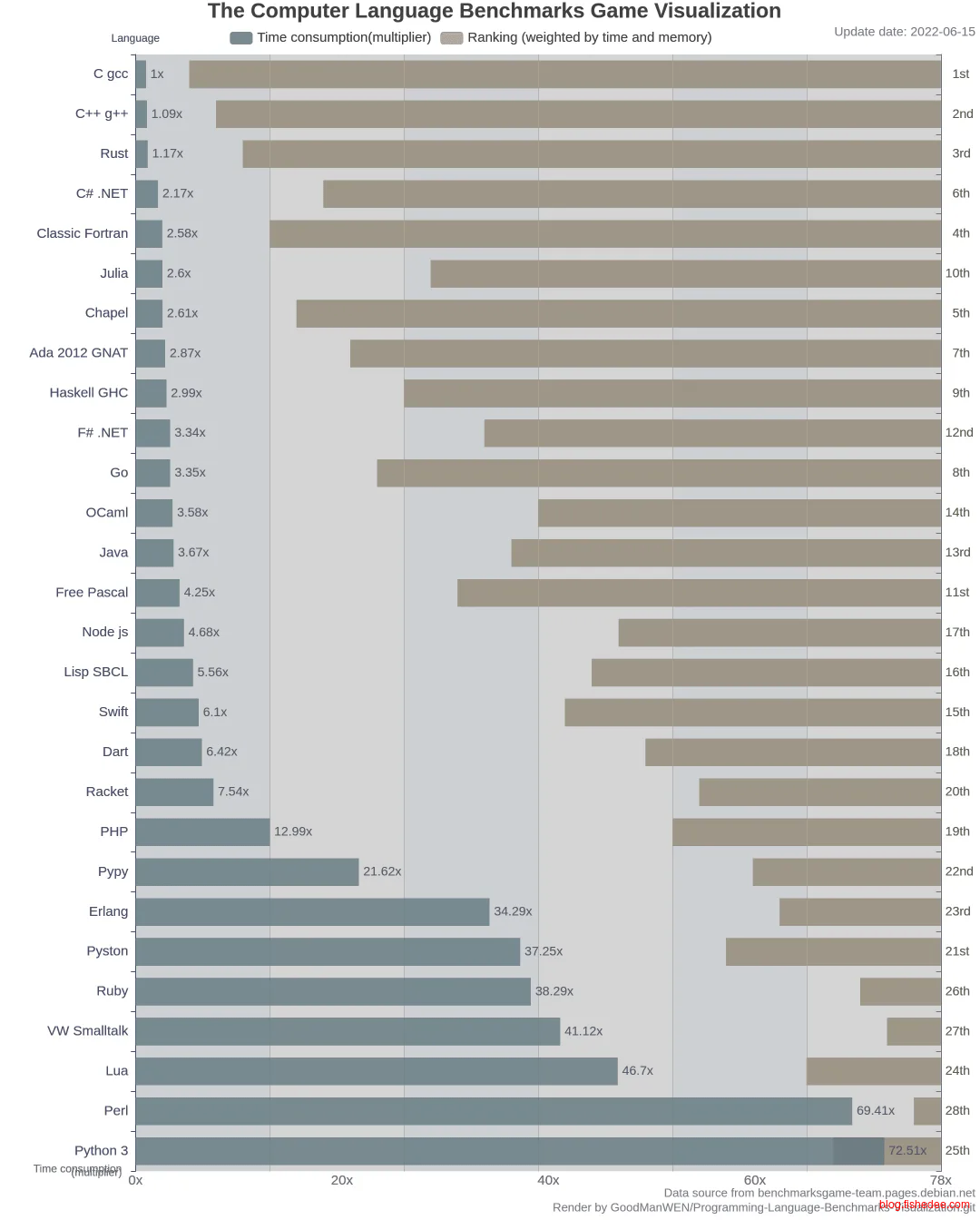
性能比较在这里
- Kotlin = java ,约为3.67x
- node js,约为4.68x
- dart,约为6.42x
总体而言,dart的性能处于最后一档,作为强类型而言,这确实有点弱。再加上语言特性加持的话,我认为TypeScript其实比dart更好,性能更好,而且也支持热更新。
- 本文作者: fishedee
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 CN 许可协议,转载必须注明出处!